基于QField的地质测绘¶
作者:Rohanna Gibson,Terrane地球科学公司的结构地质学家
目标¶
收集有关基岩地质的新数据,并查看现场现有的地质科学数据。地质测绘使用纸质地图和/或数字设备完成数据采集。目标是通过直接在外业输入数据,创建具有相同术语的高质量数据,并参考外业现有的地质科学数据,从而改进地质测绘工作流程。
工程准备¶
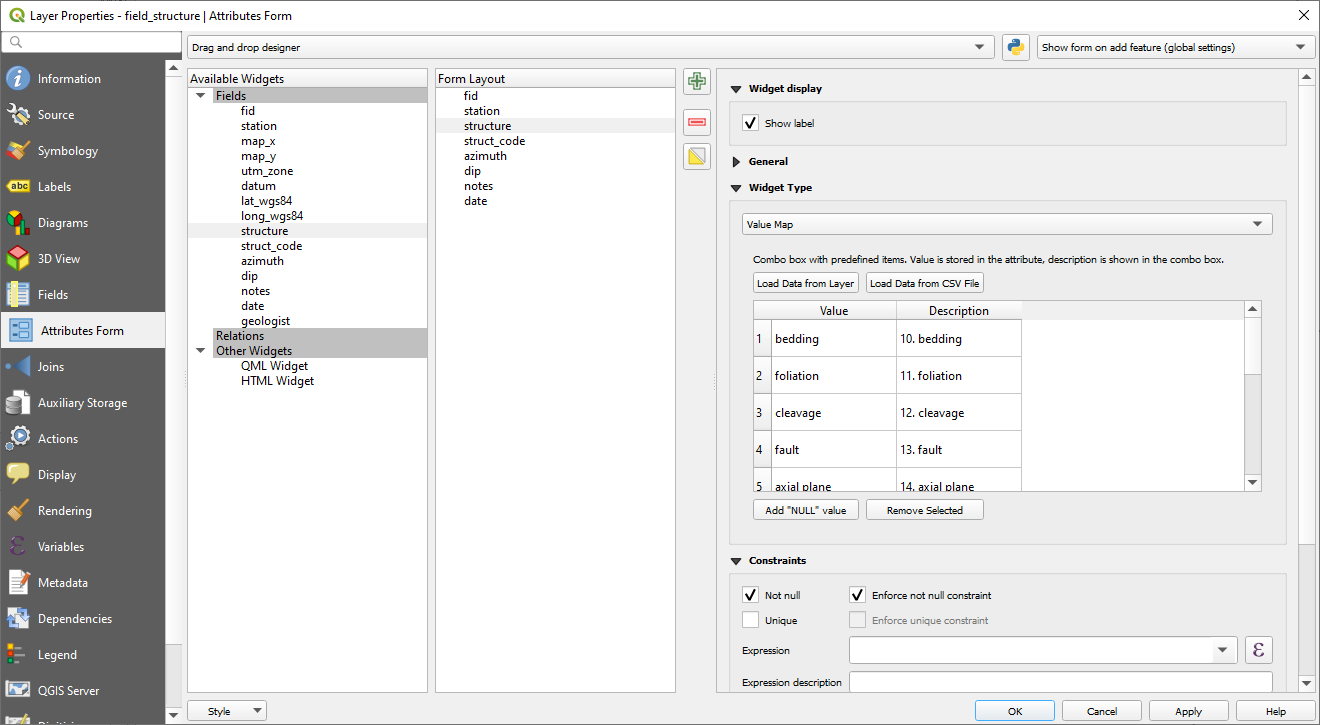
Prior to starting in QField, a geologic mapping GeoPackage was designed to collect vector data including point station, structure, photo, and sample layers as well as line and polygon layers for contacts, faults, alteration, and geology. Attribute fields are customized for ease of data entry and data quality assurance using value maps, defaults (value or expression), and constraints within the Attributes Form. For example, the structural layer includes:
坐标
Fields with default value x and y coordinates from GPS data.
结构类型
Value map (drop down list) with structural features (e.g., bedding, cleavage, lineation), set with a "not null" constraint.
方位角和倾角
Integers with range set from 0-360 and 0-90, respectively.
日期
默认值为创建要素时的当前日期和时间
为每个图层定制符号和标注,包括嵌入SVG符号,用于随 Azimuth Field 旋转的结构要素。
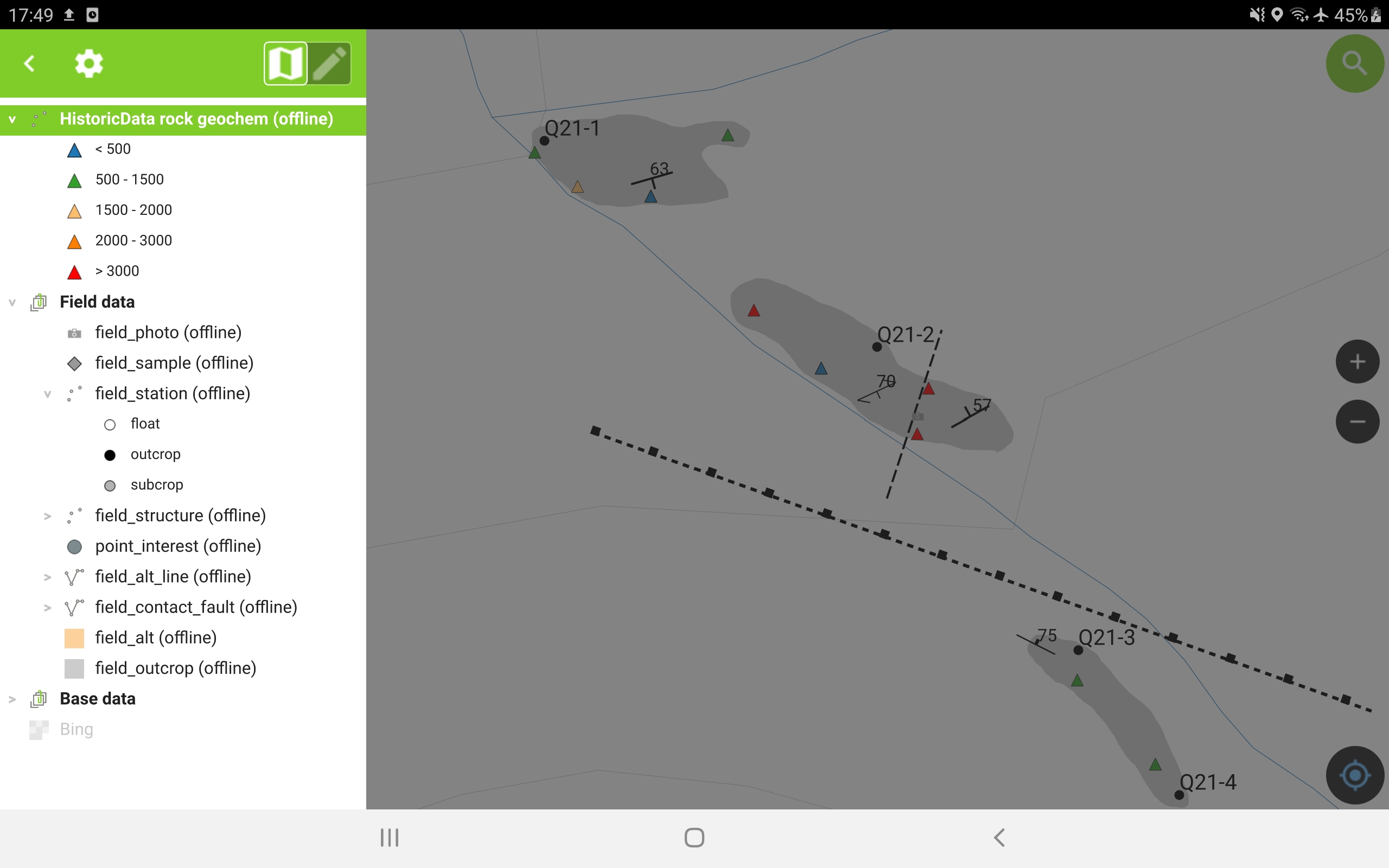
In addition to field data, base maps and historic data are compiled into GeoPackage for reference. Base maps include vector topographic data and raster orthophotos. Raster geophysical data and vector geochemical data are included if available, as well as historic geologic mapping. Map themes are designed to quickly toggle between geologic mapping, geophysics, and geochemistry views.
数据收集¶
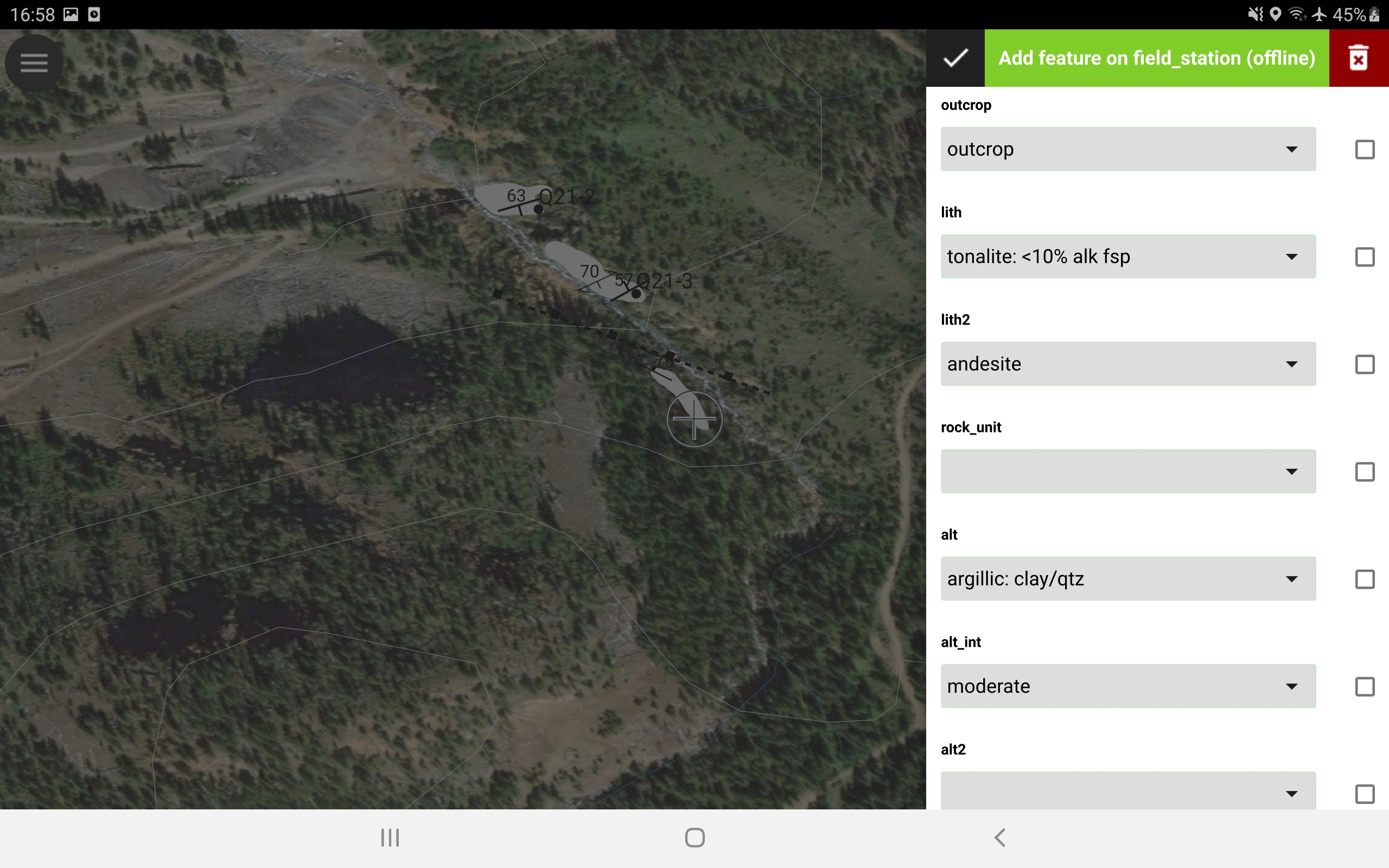
Field data collection includes adding point data for map stations, structures, photos, and samples. Polygons and lines are drawn freehand with a stylus or adding vertices manually.
Location and direction of travel are displayed using internal device GPS (or external GPS device linked via Bluetooth), historic vector and raster layers can be viewed relative to location. Current and historic vector layers can be searched and viewed in QField.
Field data are synchronized in QGIS followed by a short data clean up and verification process. The QGIS project is then exported back to QField for additional data collection.
Structural data collection may be upgraded with future development of a geologic compass feature. https://github.com/opengisch/QField/issues/1882
结论¶
Final geologic maps and analysis are prepared directly from field data sets with no need to digitize field data. Depending on proficiency and type of mapping, the QField geologic mapping workflow takes approximately the same amount of field time as manual (paper) mapping and drastically reduces office data digitization time. Additionally, historic data are easily referred to in the field, allowing for real time interpretation and targeted field work. Maps and attribute tables can be exported directly from QField or the QGIS project for daily field updates or communication between working groups.
QField allows for data integrity with customizable attribute fields and database compatibility. Field data quality assurance can be built in during project design, ensuring attributes are consistent between users and reducing human error with constraints and default values.