QFieldのストレージアクセス¶
以下は、QFieldでプロジェクトや個々のデータセットにアクセスする方法について、OSごとに説明したものです。
備考
既存のQFieldユーザーの皆様へ: セキュリティ上の理由から、Googleは2021年11月より新しいストレージアクセスルールを導入しました。ほとんどのアプリケーションは、デバイスの内部および外部ストレージのほとんどの場所にあるファイルに直接アクセスすることができません。この新しい制限の中で QFieldは、プロジェクトとデータセットをGoogle指定のストレージにインポートしなければなりません。 ストレージにインポートする必要があります。以下の説明をご参照ください。
AndroidとiOSでプロジェクトとデータセットを開く¶
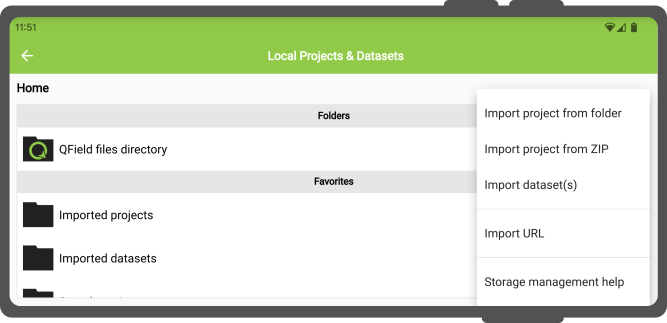
QFieldは3つの方法でプロジェクトとデータセットを開くことができます:
- URLからインポートする:
- プロジェクトフォルダをインポートする (Androidのみ):
- 圧縮されたプロジェクトファイルをインポートする (Androidのみ):
- 個別のデータセットをインポートする (Androidのみ):
これらのアクションは、QFieldのようこそ画面にある「ローカルファイルを開く」ボタンをクリックし、プロジェクト/データセット設定画面の右下にある「インポート(+)ボタン」から利用可能です
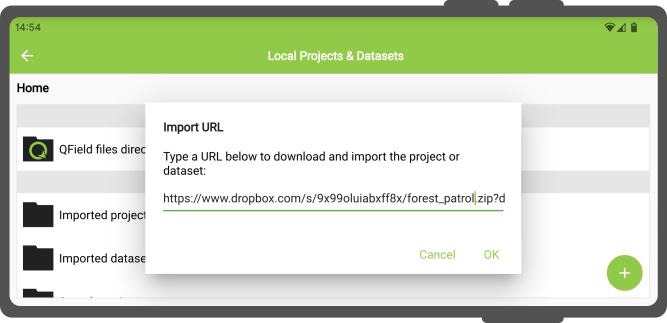
URLからインポートする¶
「インポートURL 」アクションでプロジェクトや個々のデータセットをインポートする場合、ユーザーは次のように尋ねられます。はファイルへのURL文字列を要求されます。QFieldはその内容を取得し、URLがZIPアーカイブに圧縮されたプロジェクトを指している場合、または「インポートされたデータセット」に保存されます。
QFieldは、1つ以上の.qgs/.qgzプロジェクトファイルが検出されると、ZIPアーカイブを圧縮プロジェクトとみなします。
プロジェクトフォルダーをインポートする¶
「フォルダからプロジェクトをインポート」アクションでプロジェクトをインポートする場合、QFieldがフォルダー上の指定されたフォルダーの内容を読み込む許可をユーザーに要求します。フォルダーを選択すると、QFieldはそのフォルダーをコピーします。フォルダが選択されると、QFieldはそのフォルダの内容(サブフォルダを含む)を「インポートされたプロジェクト」フォルダにコピーします。ユーザーはそこからプロジェクトを開いて操作することができます。
ドロップダウン・メニューから指定したフォルダを再インポートすると、同じフォルダ名の既存のプロジェクトは上書きされます。これにより、ユーザーはプロジェクトを更新することができます。
備考
フィーチャーの編集、追加、削除は、インポート処理中に選択された元のフォルダではなく、インポートされたプロジェクトのデータセットに保存されます。編集したプロジェクトやデータセットを送信/エクスポートする方法については、以下のセクションを参照してください。
圧縮されたプロジェクトをインポートする¶
プロジェクトは、ZIPアーカイブに圧縮されたプロジェクトを提供されることで、QFieldにインポートすることができます。「ZIPからプロジェクトをインポート」アクションを選択すると、デバイスのストレージにあるZIPファイルを選択するよう求められます。QFieldはそのファイルを「インポートされたプロジェクト」の場所に解凍します。ユーザーはそこからプロジェクトを開いて操作することができます。
これにより、単一のファイルをユーザーに送信できるため、プロジェクトのリモート展開が大幅に容易になります。
個別のデータセットをインポートする¶
「データセットをインポートする」アクションでは、Androidシステムのファイル選択ダイアログを使って、1つ以上のデータセットを選択することができます。データセットを選択すると、QFieldはそれらのデータセットを「インポートされた」フォルダにコピーし、ユーザーはそのフォルダを開いて内容を変更することができます。
備考
データセットをインポートする際、ユーザーはすべてのサブファイルが選択されていることを確認する必要があります(例えば、シェープファイルの場合、ユーザーは.shp、.shx、.dbf、.prj、.cpgファイルを選択する必要があります)。
Androidで修正したプロジェクトとデータセットをエクスポートする¶
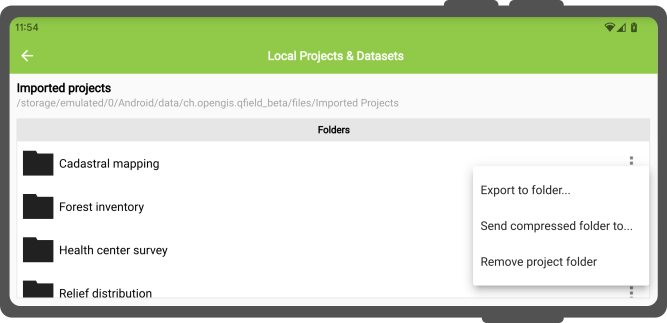
ユーザーがインポートしたプロジェクトやデータセットを修正すると、QFieldは、システムで保護されたファイルストレージからコンテンツを送信したり、エクスポートしたりするためのさまざまな手段を提供します:
- プロジェクトフォルダまたは個々のデータセットをエクスポートすることによって;
- 圧縮したプロジェクトフォルダを{クラウド、電子メール、メッセンジャーなどの}アプリに送信することによって;
- 個々のデータセットを{クラウド、電子メール、メッセンジャーなどの} アプリに送信することによって、そして
- USBケーブルでインポートされたコンテンツに直接アクセすることによって
これらのアクションは、QFieldのようこそ画面にある「ローカルファイルを開く」ボタンをクリックすることでアクセスできる、プロジェクト/データセット選択画面のプロジェクトフォルダと個々のデータセットリストにあるドロップダウンアクションメニューから利用できます。
プロジェクトフォルダまたは個々のデータセットをエクスポートする¶
「フォルダにエクスポート」アクションを選択すると、ユーザーは、Androidシステムのフォルダ選択画面を使って、選択したプロジェクトフォルダまたは個々のデータセットのコンテンツをコピーする場所を選択するよう求められます。
このアクションは、変更したプロジェクトやデータセットのコンテンツを、Syncthingのようなサードパーティの同期アプリがアクセスできるデバイス上のフォルダにコピーしたり、Androidのスコープストレージディレクトリプロバイダをサポートするプロバイダのクラウドアカウントにコンテンツを直接コピーしたりするために使用できます(執筆時点では、NextCloudアプリのみがサポートしています)。
備考
フォルダにエクスポートすると、既存のコンテンツは上書きされます。
圧縮されたプロジェクトを送信する¶
「圧縮されたフォルダを送る」アクションは、選択したフォルダのコンテンツをZIPアーカイブに圧縮します。その後、ユーザーは、結果のZIPアーカイブをデバイスのどのアプリを介して送信するかを求められます。
QFieldの「インポートプロジェクト」ディレクトリのルートフォルダを選択して、プロジェクト全体を圧縮して送信したり、プロジェクトフォルダ内のフォルダを選択して送信したりすることができます。これにより、圧縮ファイルを/DCIMサブフォルダなどに絞り込むことができます。
個別のデータセットを送信する¶
ユーザーは個々のデータセットに対して「送信先」アクションを選択することができ、編集したデータセットをGmail、Drive、Dropbox、Nextcloudなどのサードパーティアプリに直接送信することができます、
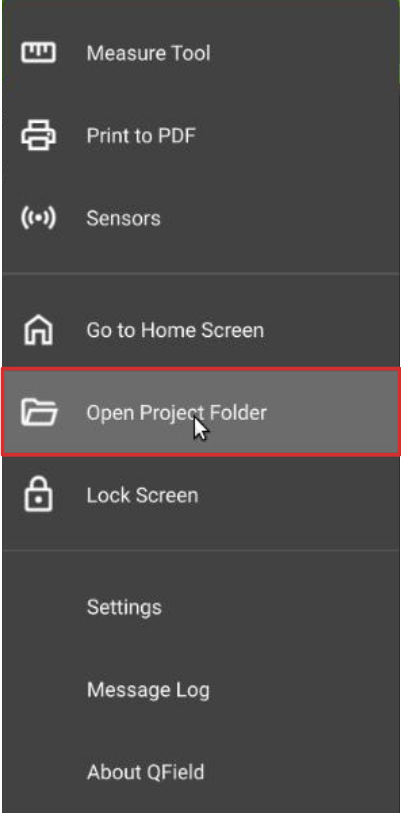
同期されたQFieldCloudプロジェクトからレイヤーをエクスポートします。これを行うには、プロジェクト内で:
- プロジェクト内の「歯車アイコン」をクリックします。
- 「プロジェクトフォルダを開く」を選択します。
-
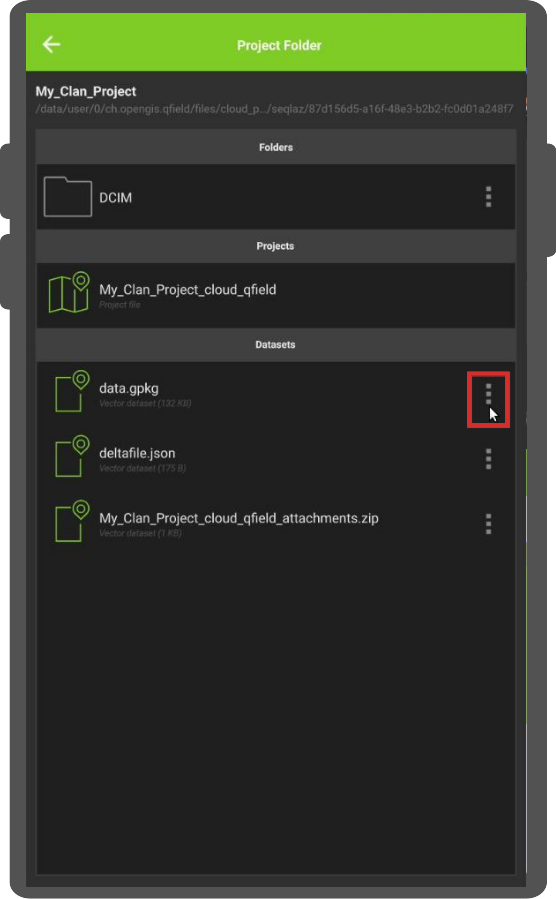
このプロジェクトフォルダの中に、プロジェクトファイルがあります。オフラインレイヤーは'data.gpkg'という名前のファイルに保存されます。また、添付ファイル(写真、オーディオ、ビデオなど)をエクスポートすることもできます。
-
次に、ファイルまたはフォルダの右側にある3つの点(⋮)をクリックします。
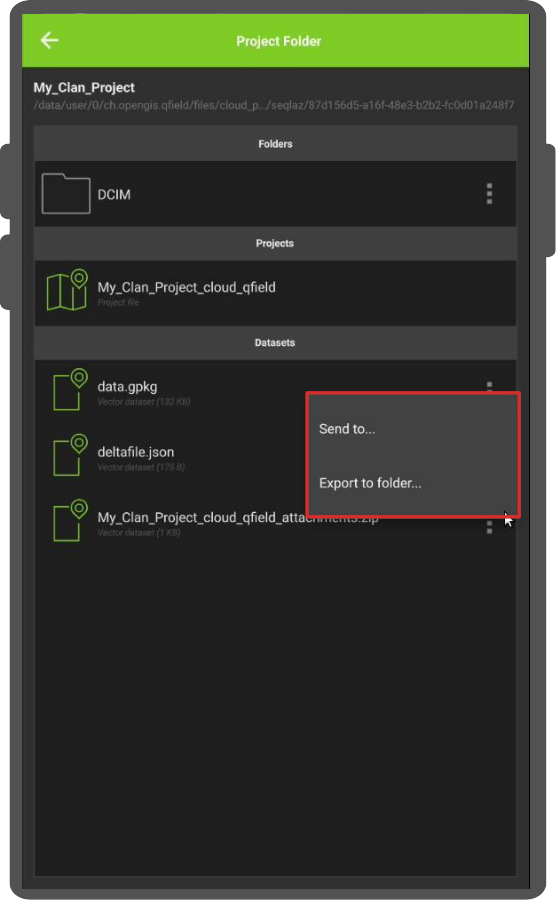
- '送信先...'または'フォルダにエクスポート...'アクションのいずれかを選択し、お好みに応じてプロンプトに従ってください。
備考
この機能はアンドロイドでのみ利用可能です。
USBケーブルを使ってインポートされたコンテンツに直接アクセスする¶
Android¶
インポートしたプロジェクトやデータセットには、USBケーブルを使って直接アクセスできます。場所は、プロジェクト/データセット選択画面の上部ナビゲーションバーに表示されます。
USBケーブルでコンピュータに接続されたほとんどのデバイスでは、パスは <drive>:/Android/data/ch.opengis.qfield/files/になります。インポートされたデータセットフォルダとインポートされたプロジェクトフォルダがあり、その中にインポートされたプロジェクトとデータセットがあります。プロジェクトの内容とデータセットに加えられた変更は、この場所にあるファイルに保存されます。
iOS¶
インポートしたプロジェクトとデータセットは、WindowsとmacOSのiTunesを使ってQFieldアプリケーションフォルダに移動し、USBケーブルを使って直接アクセスすることができます。Linuxでは、'libimobiledevice'からアクセスできます。