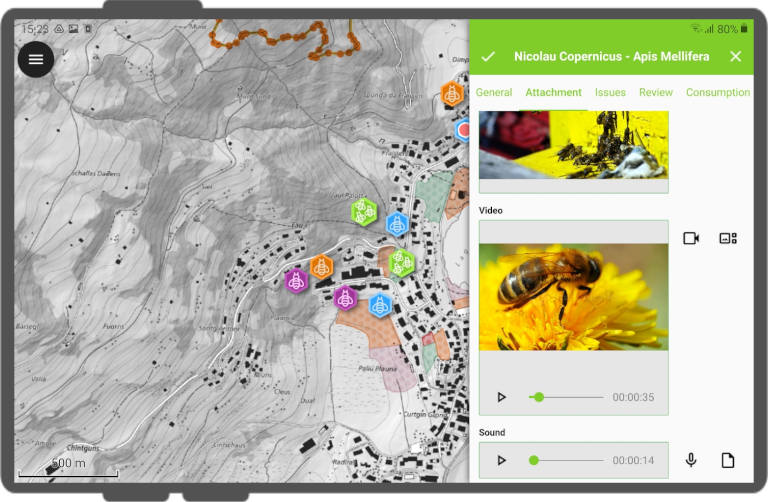
Use attachment¶
In QField, a field with Attachment widget can be used to:
- Show and take photos
- Show and record videos
- Listen and record sound clips
- Show links to external files like PDFs or documents
To configure the Widget, please refer to the Attributes Form Documentation
Add a series of pictures to a feature¶
Desktop preparation
One or more pictures can be added to the feature. Here is an example of how to proceed.
Tables¶
It is necessary to set up two tables. One table where the features are stored and one with a list of pictures.
Apiary¶
| Field | Type |
|---|---|
id |
Text (UUID) |
geometry |
Geometry |
... |
Apiary_pictures¶
| Field | Type |
|---|---|
id |
Text (UUID) |
apiary_id |
Text (UUID) |
path |
Text |
... |
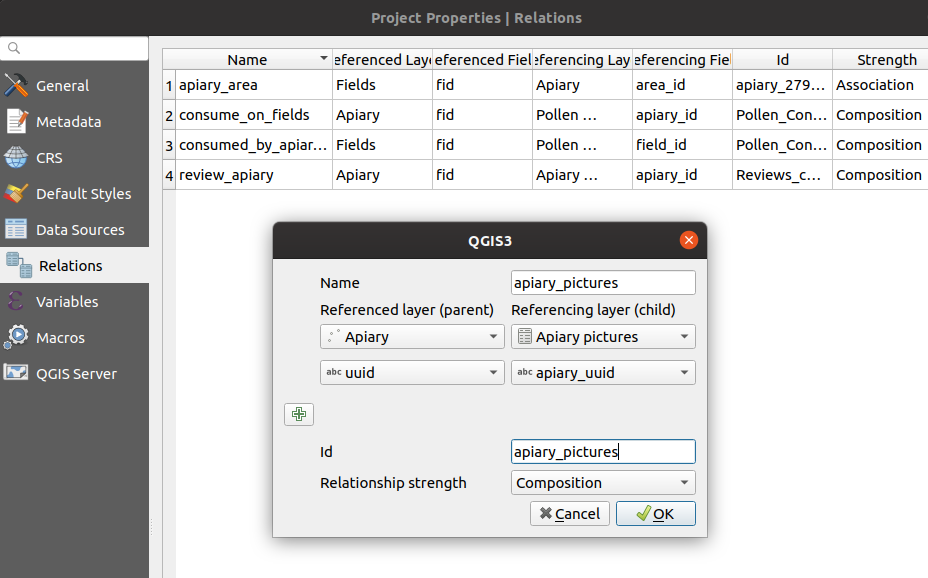
Relations¶
Create a relation with:
apiaryReferenced layeridReferenced fieldapiary_pictureReferencing layerapiary_idReferencing fieldstrengthComposition
Widgets¶
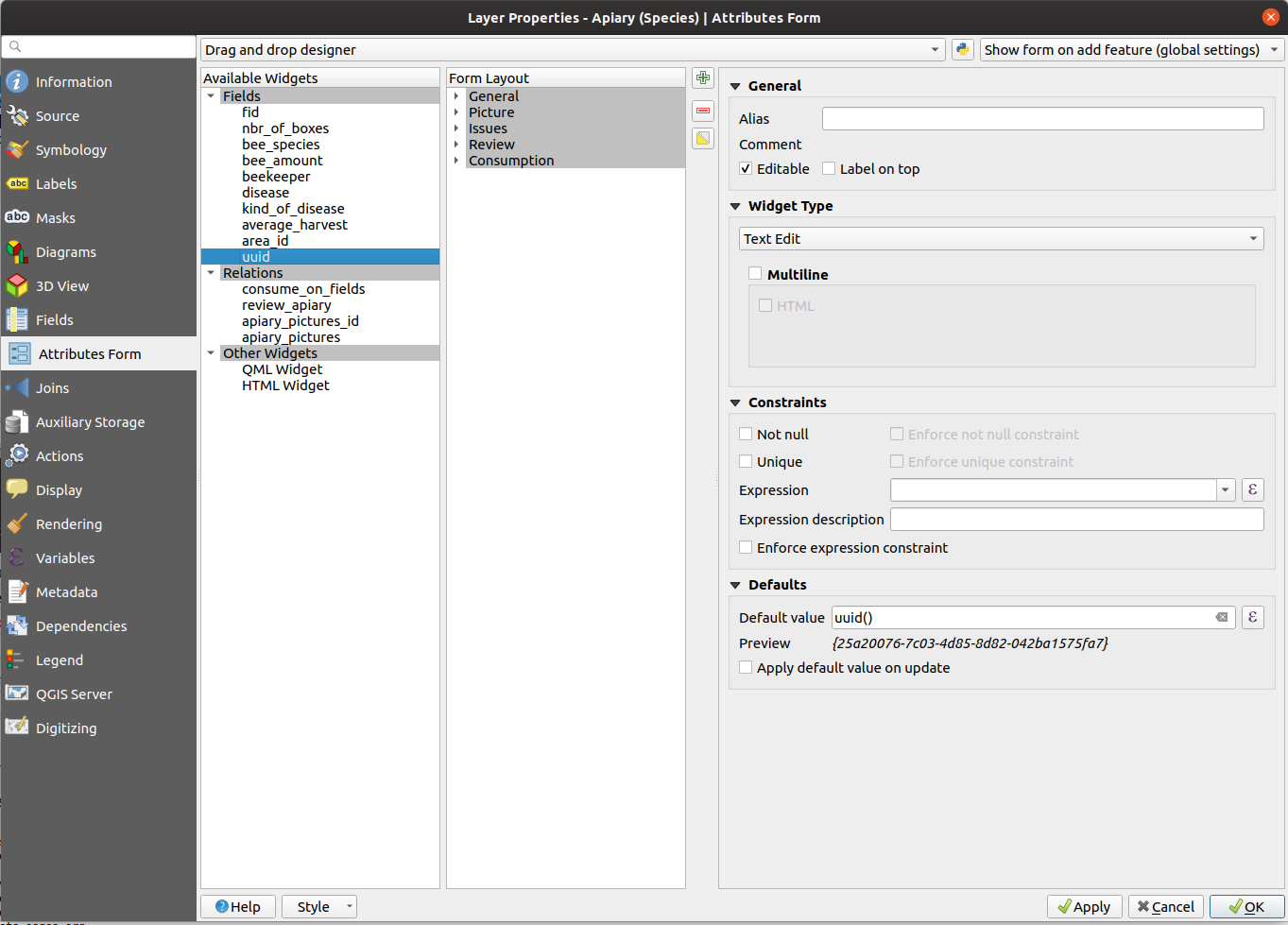
Apiary¶
You can either choose the Text Edit or UUID Generator widget.
Its default value in any case has to be uuid('WithoutBraces').
Hide it from the view as it should not be edited by the user.
Set the relation widget to many to one relation and add the relation to the form
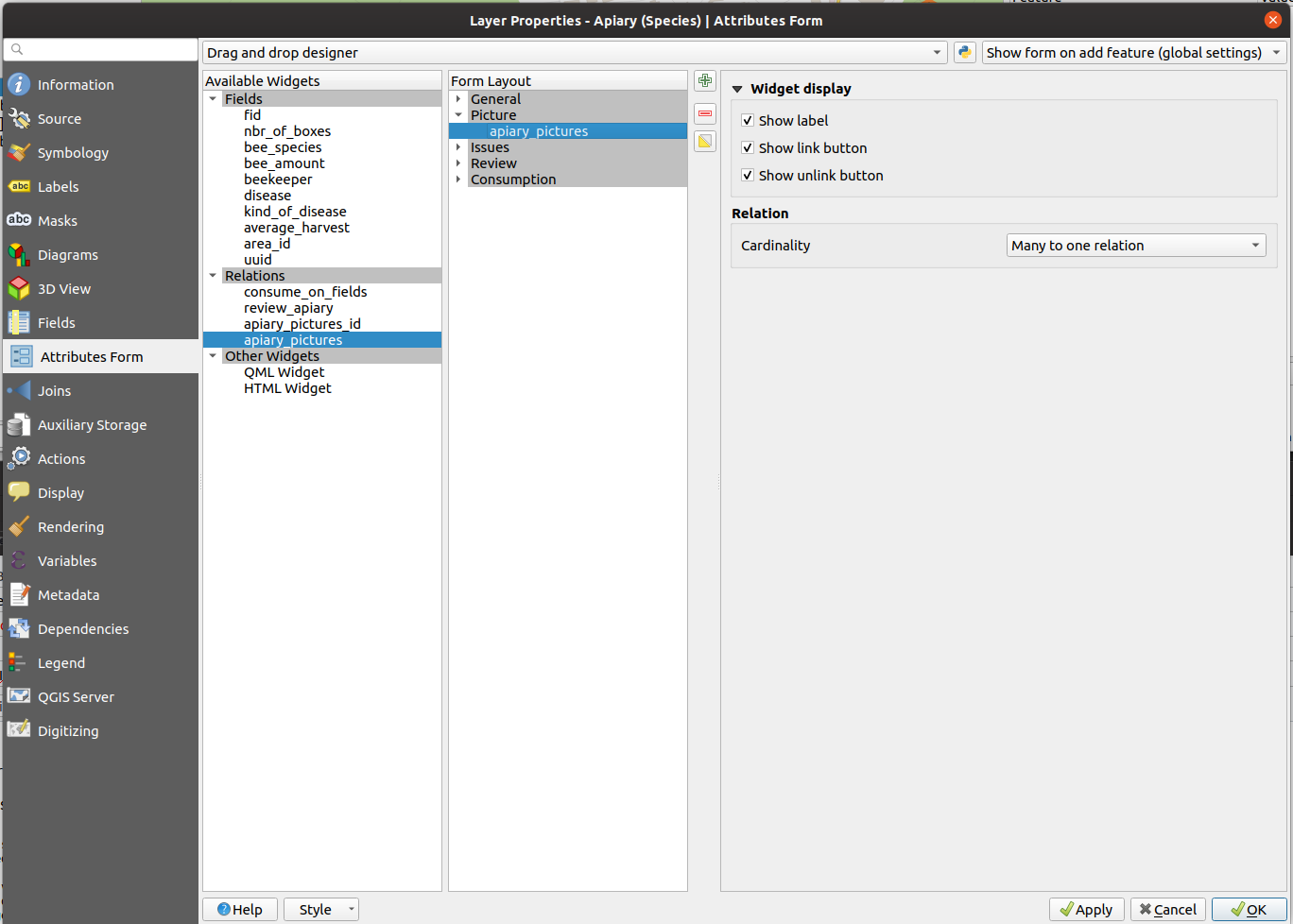
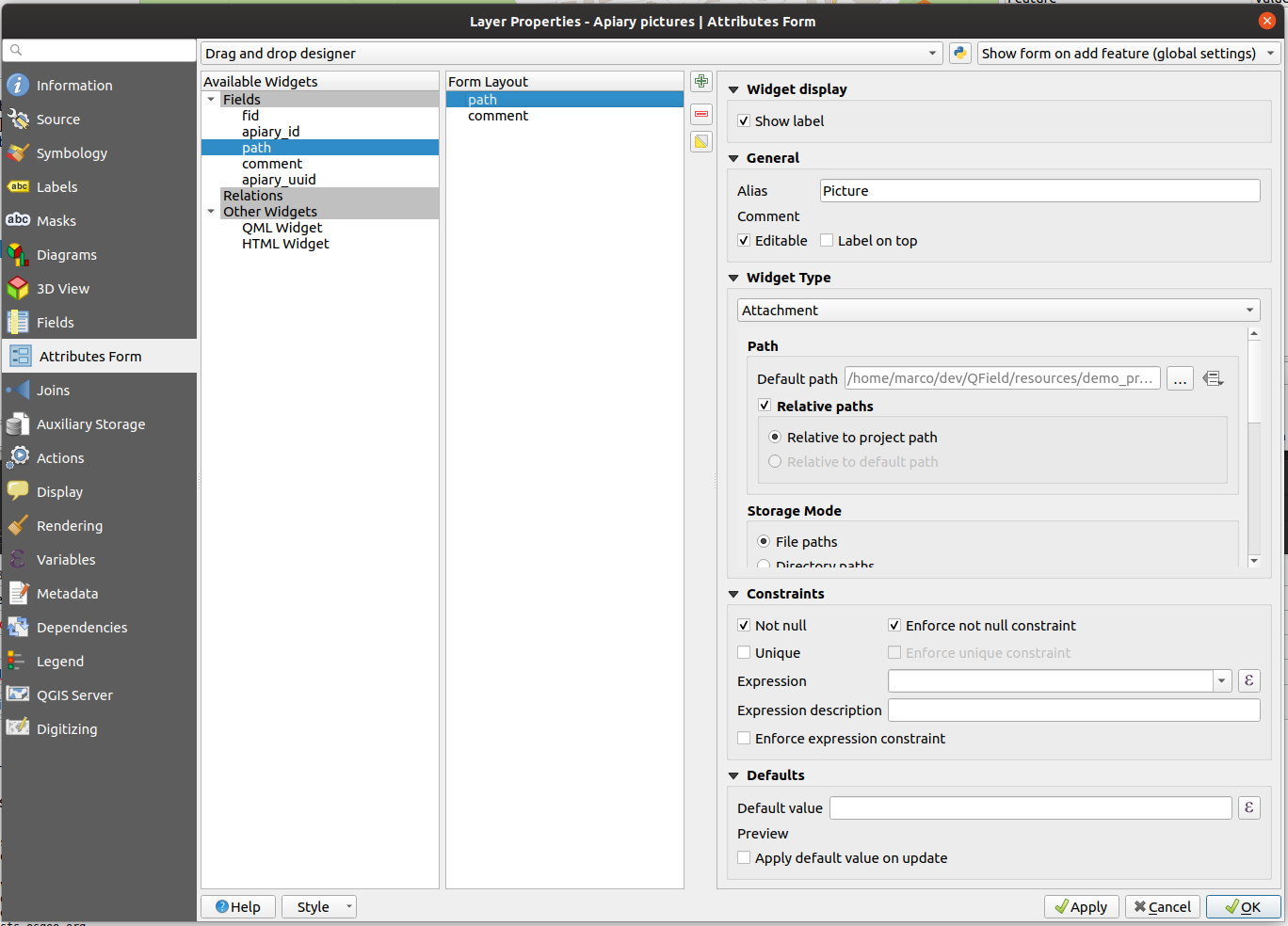
Apiary picture¶
Set the widget type of the field path to Attachment and add it to the form
Drawing and sketching¶
QField has an in-app drawing and sketching functionality enabling you to directly sketch over and annotate images captured while in the field as well as drawing on top of a blank canvas or over a template.
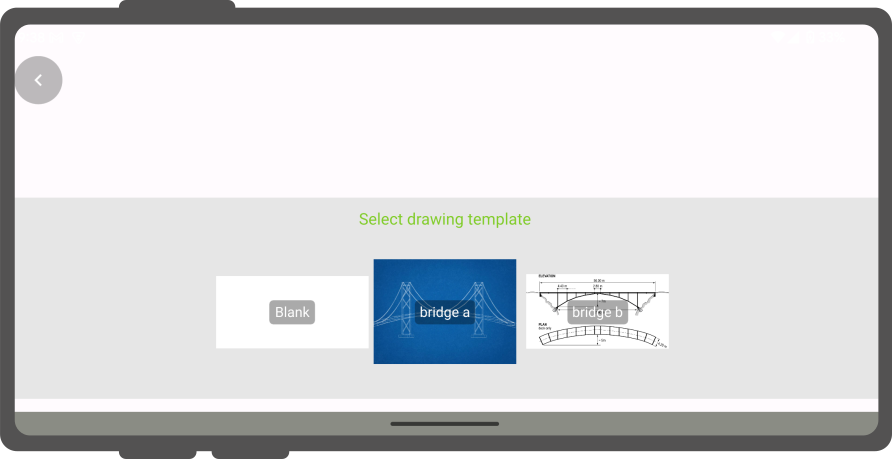
Drawing templates¶
On top of annotating captured images, QField supports drawing from image templates. The following two methods are available to add templates:
- The first method is to create a
drawing_templatesfolder located alongside a project file and populate it with images. Whenever that project is loaded, QField will register all images within that folder as drawing templates. - Alternatively, you can add images into the
drawing_templatesfolder found inside your QField app folder. If you are not familiar with that app folder, its location is shown at the bottom of the About QField overlay.
Templates shipped alongside projects as well as the QField app folder will be shown when users choose "Draw a sketch" by pressing the (⋮) menu icon of the attachment widget.
Geotagging¶
Fieldwork
QField's internal camera will automatically geotag your pictures.
Information about location and direction of the pictures will therefore be baked into the image file.
Note
While with older Android versions it was possible to use other apps like the amazing OpenCamera app for taking pictures and preserving EXIF information from there, this is no longer with recent Android versions. Is recommended to disable Use native Camera in the settings to preserve EXIF information.
Image Stamping¶
QField allows you to add image stamping. This is configured directly from the QFieldSync plugin in QGIS. With this functionality you can add detailed and formatted information when taking photos in the field.
Styling Settings¶
Desktop preparation
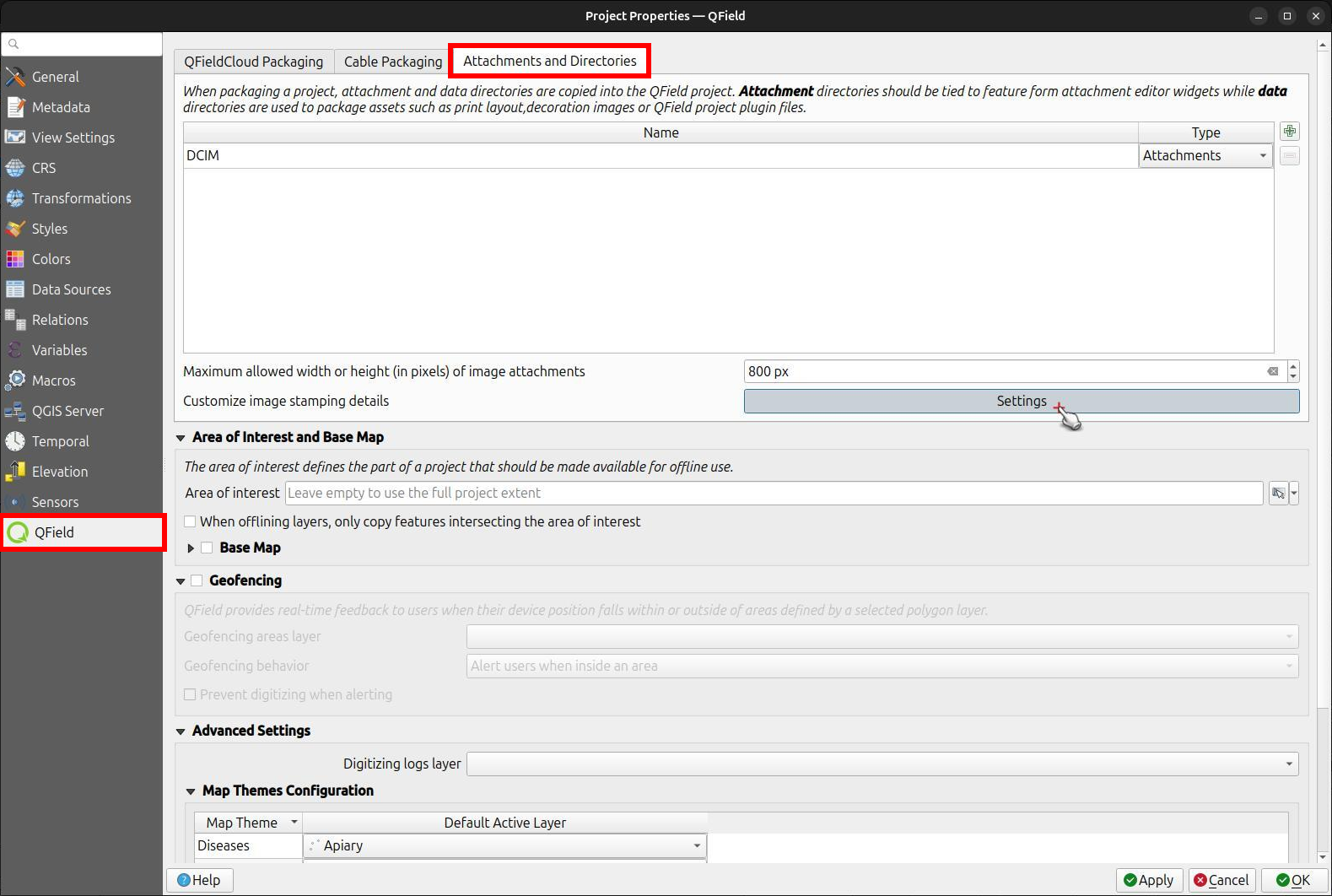
Navigate to the Project > Properties > QField > Attachments and Directories sub-panel and click on "Settings" for "Customize image stamping details".
You can add the following settings:
-
Font and Alignment: You have full control over the appearance of the stamped text, including the font style (color, size, drop shadow) and horizontal alignment (left, center, or right).
-
Image Decoration: Add a custom image overlay, such as a logo or a watermark, on top of the captured image.
-
Force Stamping: This option enforces image stamping, ensuring that all images collected for the project have the required information overlaid, regardless of the individual QField app settings.
-
Stamp Details: Craft a multiline string using QGIS expressions to define the information stamped on the image. A default template is provided to get you started, which includes common variables like date, time, and GNSS information.
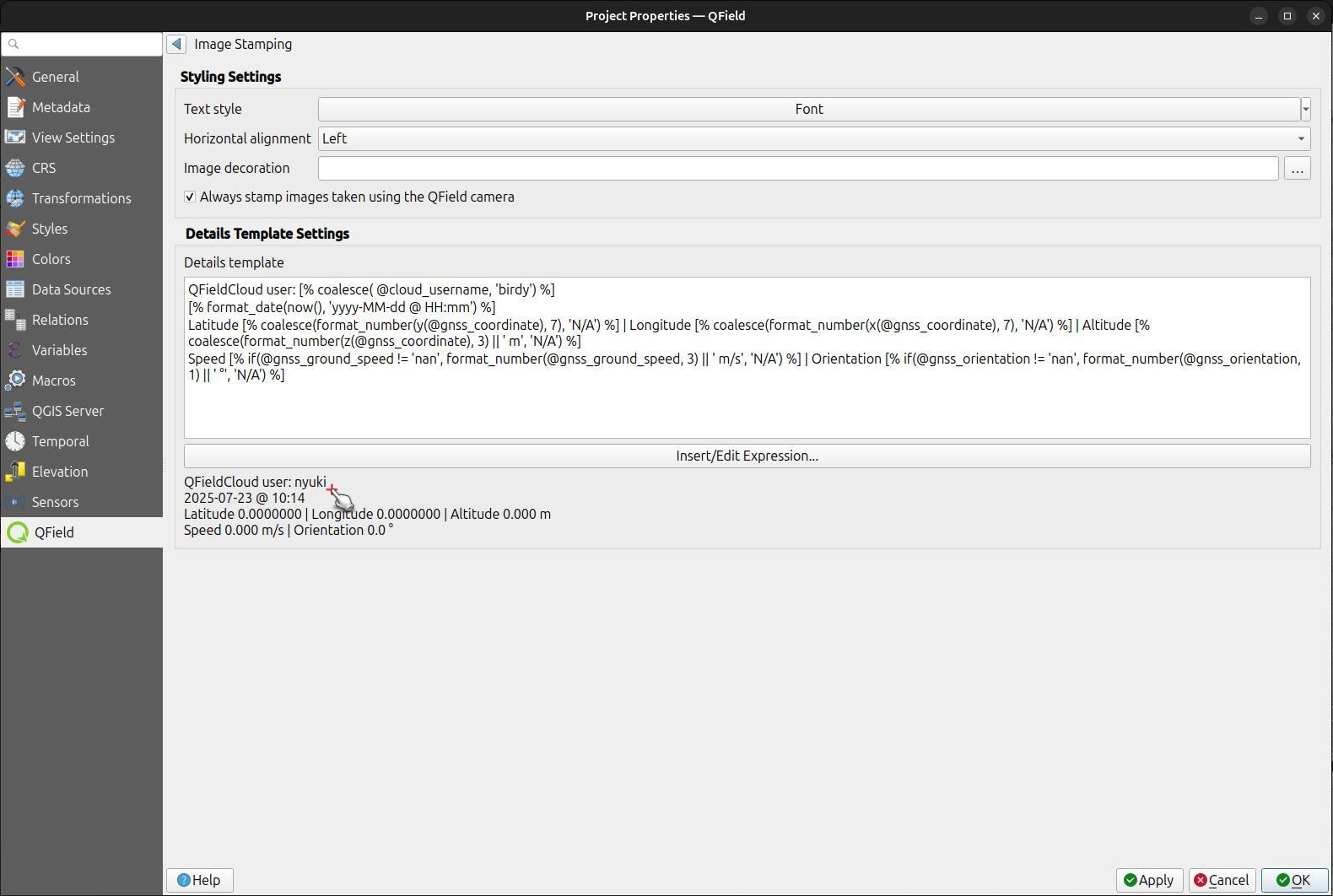
Default Template:
[% format_date(now(), 'yyyy-MM-dd @ HH:mm') %]
Latitude [% coalesce(format_number(y(@gnss_coordinate), 7), 'N/A') %] | Longitude [% coalesce(format_number(x(@gnss_coordinate), 7), 'N/A') %] | Altitude [% coalesce(format_number(z(@gnss_coordinate), 3) || ' m', 'N/A') %]
Speed [% if(@gnss_ground_speed != 'nan', format_number(@gnss_ground_speed, 3) || ' m/s', 'N/A') %] | Orientation [% if(@gnss_orientation != 'nan', format_number(@gnss_orientation, 1) || ' °', 'N/A') %]
Example
Fetching Geotags (EXIF) from the image file into the attribute table¶
Desktop preparation
Sometimes you might be interested in automatically storing Geotags such as the latitude, longitude, orientation, etc. This information is also known as EXIF tags.
To store the EXIF information, follow these steps:
- Add an attribute per EXIF tag in the table that contains the pictures.
- In the pictures form, configure the default value of each attribute to the corresponding EXIF expression See QGIS EXIF function, and make sure Apply on update is activated.
- The EXIF tags that QField can capture are listed in the QGIS documentation (link above). However, this list might slightly vary depending on the mobile characteristics.
- Capturing EXIF tags requires accessing the full physical path of the picture.
Be sure to reflect this in the QGIS expression.
For example, the expression
exif(@project_folder + '/' + "path", 'Exif.Image.Orientation')retrieves the orientation of the picture stored in path. For more tags visit the QField EXIF reference documentation and the exiv library documentation. - Completed! QField now captures and stores the EXIF tags in the pictures table while taking pictures.
Maximum picture size¶
Desktop preparation
The advanced settings allow rescaling the photos to a maximum width/height in Project > Properties > Attachments and Directories
Configurable attachment path¶
Desktop preparation
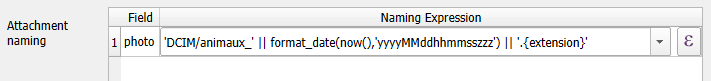
QFieldSync provides the possibility to configure the path and the file names of picture attachments.
- Go to Vector Layer Properties > QField
- Choose the layer, the field and configure the expression
Use expressions to specify the path of the attachments. By default, pictures are saved into the "DCIM" folder, audio are saved into the "audio" folder and videos are saved into "video" with a timestamp as name.
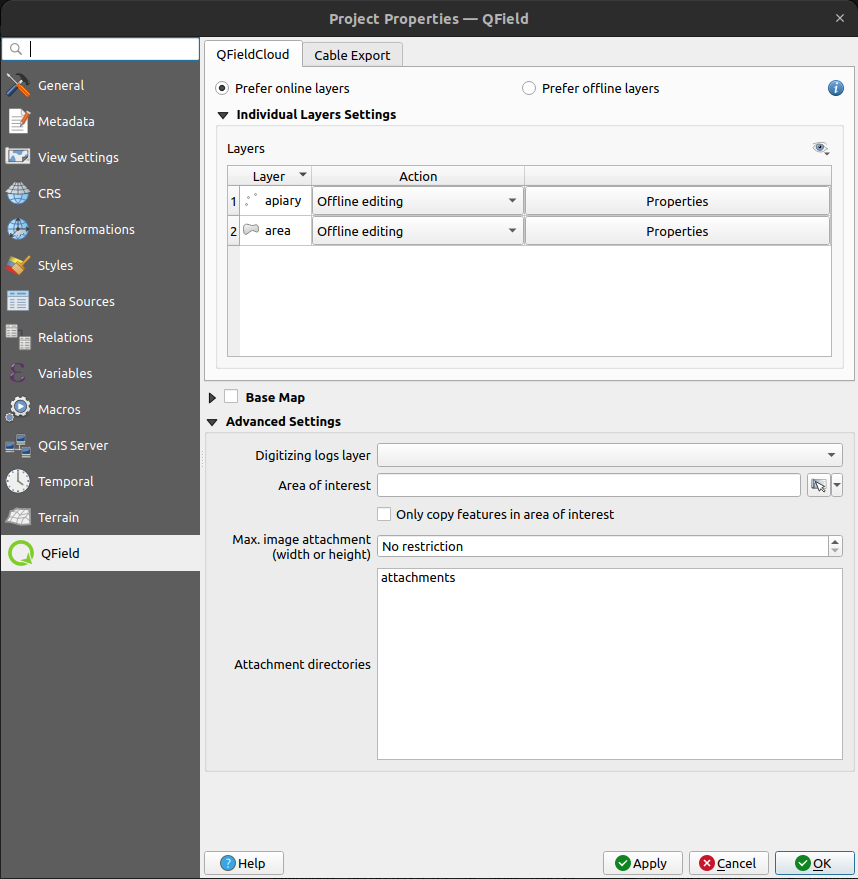
Additional directories can be synchronized with pictures or other attachments. Extra paths can be configured in Attachment and Directories tab in the QFieldSync settings under Project > Properties > QField. All paths are relative to the project directory.