Service PostgreSQL¶
A pg_service.conf file allows to use an named alias for a PostgreSQL server connection.
Instead of storing hostname, port, database name and more into the QGIS Project file, these can be stored separately.
It is even possible to store username and password in a pg_service.conf file, to avoid having this stored in clear text in the QGIS Project.
Read more about PostgreSQL services in the QGIS documentation.
QField - Connexion directe¶
If you directly connect from QGIS to your database you can make use of a pg_service.conf file by placing it in the QField data folder.
You can place your file either on the Internal Device Storage or on the SD Card Storage.
You can check the path for the QField data folder in the bottom of the About QField screen in the app.
Usually the path on Android devices looks something like this: /Android/data/ch.opengis.qfield/files/QField.
Note
Unlike on *NIX systems where the file is named .pg_service.conf, the file on Android is named pg_service.conf without a leading dot sign (.).
QFieldCloud¶
QFieldCloud support pg_service.conf configurations too.
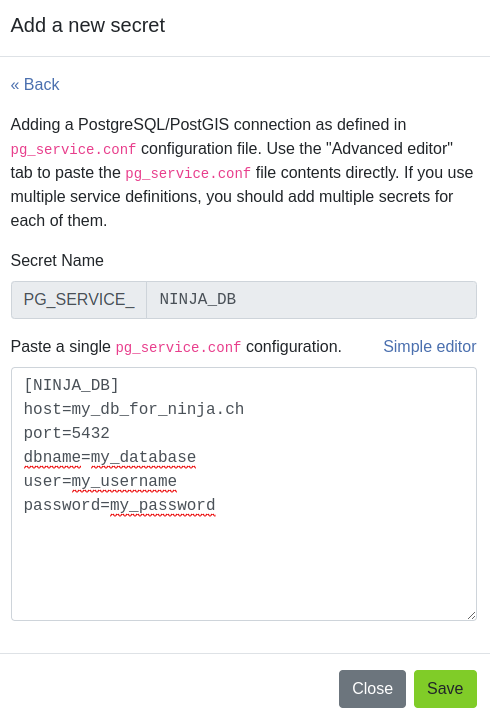
You need to configure your PostgreSQL layers with "Offline editing" cloud action and store your service settings on QFieldCloud Project's Secrets page.
Read more how to configure PostgreSQL service in the QFieldCloud documentation.
Creating a pg_service.conf File for PostgreSQL Connection in QGIS and Secrets¶
Before beginning, ensure that your PostgreSQL database allows connections from QFieldCloud. Refer to Technical specs for instructions.
Setup pg_service.conf File¶
We first need to set up a configuration file. There are many options to organize this, read more in the PostgreSQL documentation or follow the description below.
-
Créer un fichier de configuration:
-
Pour Windows: Créer un fichier intitulé
pg_service.confet le stocker à l'emplacement souhaité. -
Pour Linux/MacOS/Unix: Créer un fichier intitulé
.pg_service.confqu'il faudra placer dans le dossier d'accueil (~). -
Define Connection Parameters:
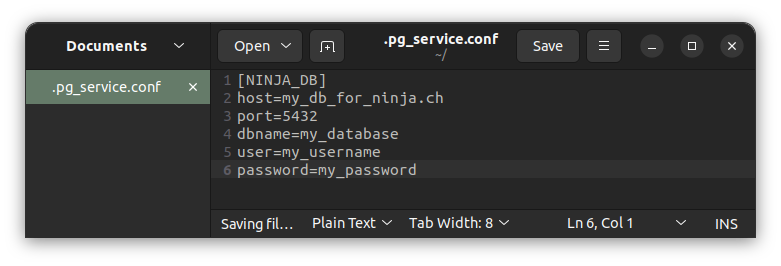
Within the file, specify connection parameters for your PostgreSQL database using the following format:
[SERVICE_NAME]
host=your_host_or_ip
port=your_port
dbname=your_database_name
user=your_username
password=your_password
Replace placeholders (your_host_or_ip, your_port, your_database_name, your_username, your_password) with actual connection details and save the file.
Additional Configuration Steps for Windows¶
-
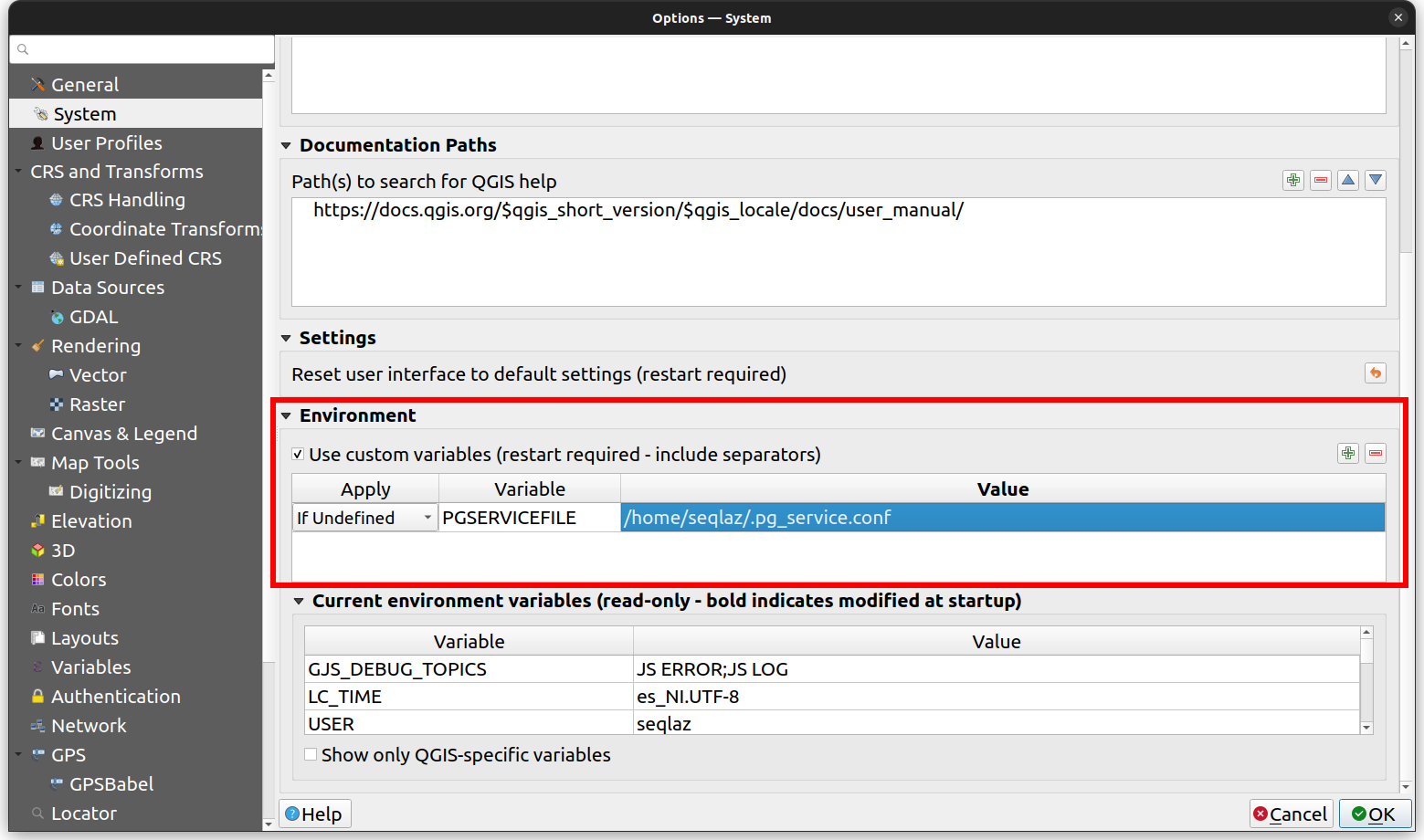
Set Environment Variable: To ensure QGIS recognizes
pg_service.conf, create an environment variable pointing to its location: -
Navigate to This PC or My Computer > Properties > Advanced System Settings > Environment Variables.
- Ajouter une nouvelle variable:
- Nom de la variable :
PGSERVICEFILE - Contenu de la variable :
C:\Users\<YourUsername>\AppData\Roaming\postgresql\pg_service.conf(soit le chemin vers votre fichierpg_service.conf).
- Nom de la variable :
Alternatively, you can set environment variables directly in QGIS via Settings > Options > System > Environment. Refer to QGIS System Settings for details.
-
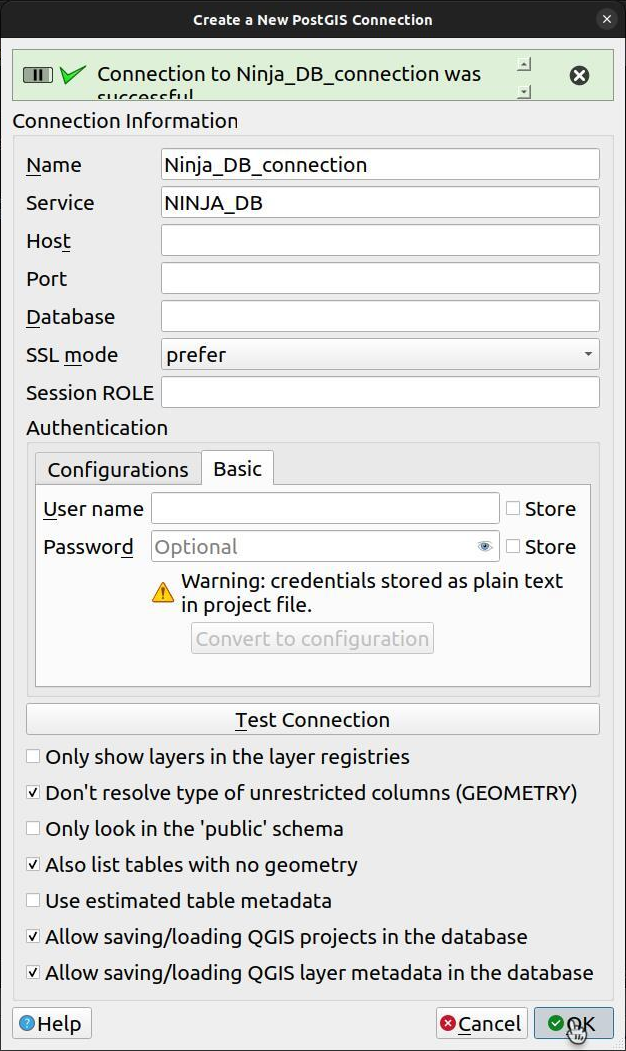
Test the Connection in QGIS: Open QGIS and set up a new PostgreSQL connection using the service name defined in
pg_service.conf(e.g.,[MY_QGIS_DB]) in the connection details. QGIS will read configuration frompg_service.confautomatically. -
Ouvrir QGIS.
- Go to Layer > Add Layer > Add PostGIS Layers...
- In Create a New PostGIS Connection, select "Service" from the drop-down menu.
- Entrer le nom du service depuis
pg_service.conf(e.g.,[NINJA_DB]) dans le champs "Service". - Cliquer sur "OK" pour vous connecter à votre base de données PostgreSQL en utilisant les informations de connexion contenues dans le fichier
pg_service.conf.
- Add Parameter to QFieldCloud Secrets: Navigate to the project's secrets page and copy the service directly from
.pg_service.confto the secret. Follow Secrets for guidance.