Ortung (GNSS)¶
QField kann das interne GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System, wie GPS, GLONASS, Galileo oder Beidou) nutzen. QField kann auch eine Verbindung mit externen Antennen durch NMEA-Streams über Bluetooth, TCP oder UDP Verbindung herstellen.
GNSS-Geräte sind in der Lage, neben der aktuellen 2D Position auf der Erdoberfläche auch die Höhe zu messen.
Visualisierung¶
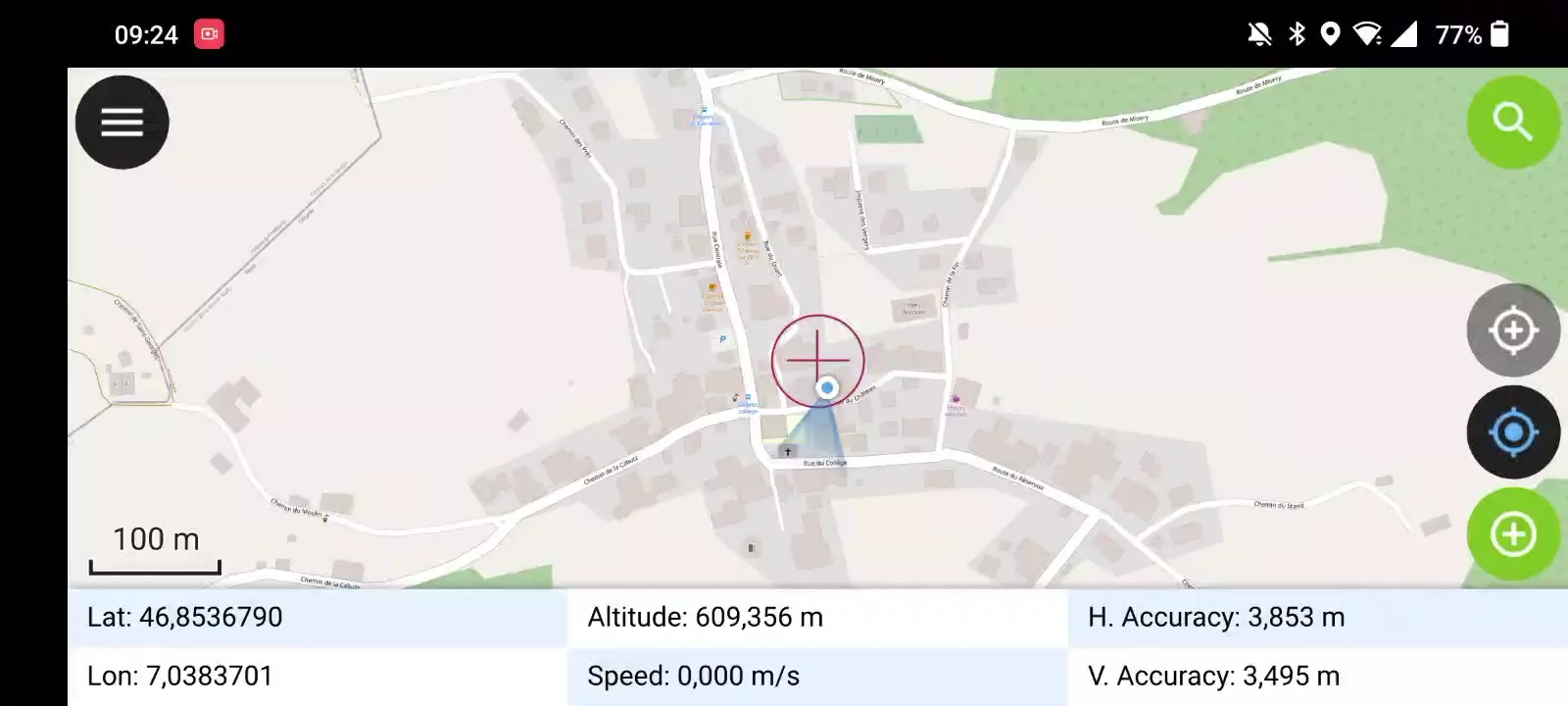
Wenn die Ortung aktiviert ist, wird Ihre Position in blauer Farbe auf der Karte angezeigt. Ihre Position ist entweder als blauer Punkt sichtbar, wenn Sie stillstehen, oder als Pfeil, der Ihre Bewegungsrichtung anzeigt wenn Sie sich bewegen.
Der blaue Strahl zeigt die aktuelle Ausrichtung Ihres Geräts an, wenn das Gerät über einen einen integrierten Magnetkompass verfügt.
Ein Kreis um die aktuelle Position zeigt die Genauigkeit an, die vom Ortungsgerät gemeldet wird.
Konfiguration¶
Die folgenden Einstellungen sind auf der Registerkarte "Positionierung" der QField-Einstellungen verfügbar.
Messung Wert (M)¶
Wenn eine Geometrie auf eine Vektorebene digitalisiert wird, die ein M-Wert enthält, fügt QField automatisch Messwerte zu einzelnen Knotenpunkten hinzu, wenn der Koordinatencursor an der aktuellen Position eingerastet ist.
Standardmäßig gibt der Wert den Zeitstempel der erfassten Position an (Millisekunden seit der letzten Messung). Sie können diesen Wert über das Kombinationsfeld auf der Registerkarte "Positionierung" der Einstellungen ändern.
Zur Auswahl stehen folgende Werte: Zeitstempel, Geschwindigkeit über Grund, Peilung, horizontale und vertikale Genauigkeit sowie PDOP, HDOP und VDOP.
Genauigkeitsanforderung¶
Es kann eine gewünschte Mindestgenauigkeit für Messungen festgelegt werden. Die Qualität wird in drei Klassen angegeben: schlecht (rot), ok (gelb) und ausgezeichnet (grün). Diese Farben werden als Punkt oben auf der GNSS-Schaltfläche angezeigt.
Die Schwellenwerte können auf der Registerkarte "Positionierung" der Einstellungen festgelegt werden.
Wenn die Einstellung Genauigkeitsanforderung aktivieren aktiviert ist, können Sie keine neuen Messungen durchführen, wenn der Koordinatencursor auf die aktuelle Position mit einem schlechten (roten) Genauigkeitswert fixiert ist.
Höhenausgleich der Antenne¶
Die Höhe des verwendeten Antennenstange kann in den Einstellungen festgelegt werden. Jede gemessene Höhe wird um diesen Wert korrigiert.
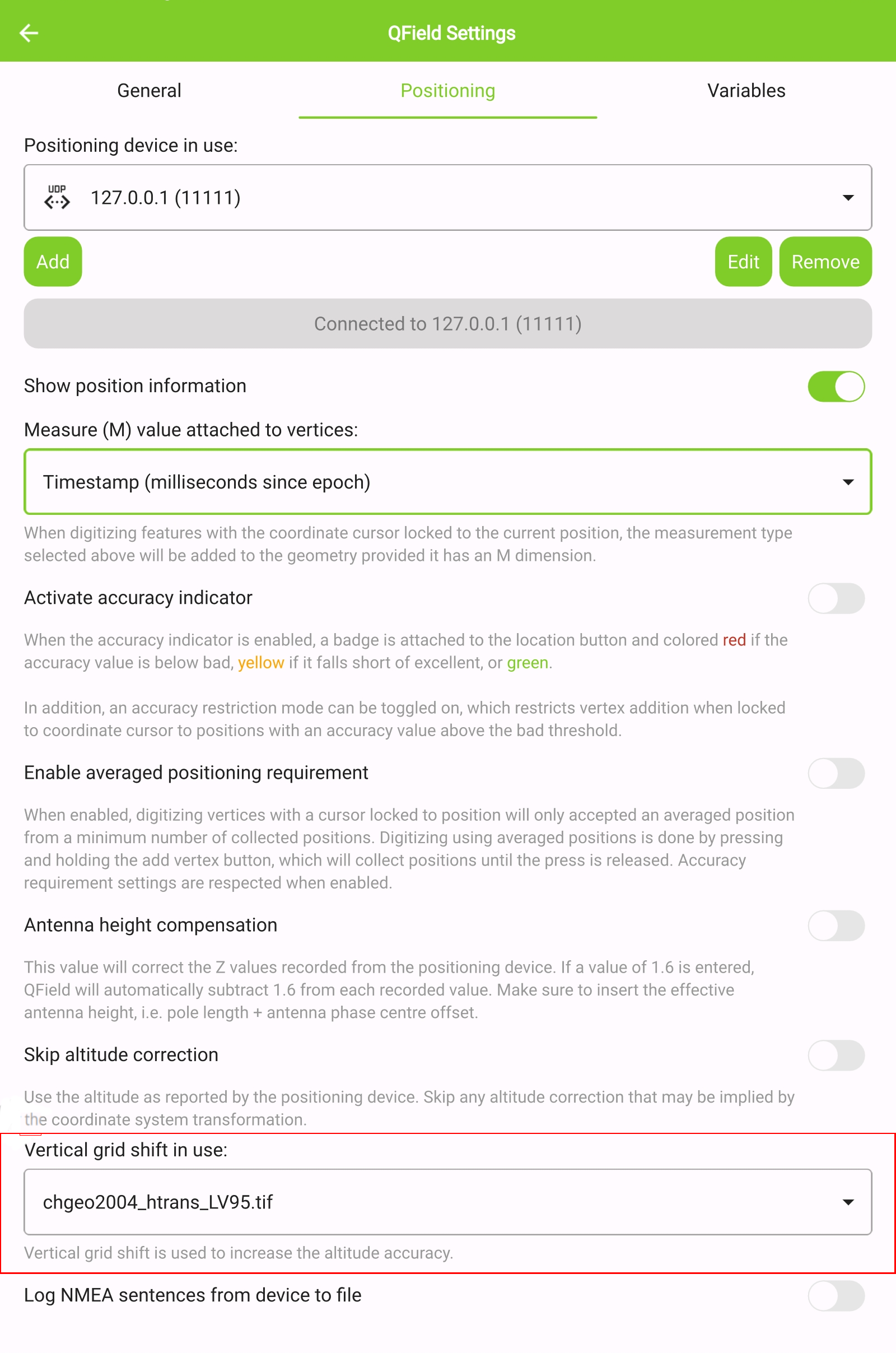
Höhenkorrektur / vertikale Gitterverschiebung¶
Die Höhenwerte können mit vertikalen Raster Grid Dateien korrigiert werden, um orthometrische Höhe zu berechnen.
Vertical grid shift files have to be made available to QField by putting them into the QField app folder [App Directory]/QField/proj.
Sobald die Geoid-Datei dort platziert ist, ist sie in QField in den Positionierungseinstellungen unter Geoid in Gebrauch verfügbar.
Wenn Sie die Höhenkorrektur via Geoid verwenden und ein externes Positionierungsgerät eingesetzt wird, sollten Sie die Option Orthometrische Höhe vom Gerät verwenden deaktivieren.
Die aktuell unterstützten Dateiformate sind:
- GeoTIFF (.tif, .tiff)
- NOAA Vertical Datum (.gtx)
- NTv2 Datum Grid Shift (.gsb)
- Natural Resources Canada's Geoid (.byn)
Workflow
Example: Netherlands - ETRS89 to NAP
For transformations involving the Dutch NAP (Normaal Amsterdams Peil) vertical datum, you'll need the official grid file from NSGI.
- Download the file: Get
nlgeo2018.gtxdirectly from the NSGI website. - Place the downloaded
.gtxfile into the directory [App Directory]/QField/proj. This is independent of whether you are using QFieldCloud or not.
Example: Switzerland - CH1903+/LV95
To get precise altitude data for Cadastral Surveying in Switzerland (LV95), you must use the geoid correction grid from Swisstopo.
The official file comes in an .agr format and must be converted to .gtx (NTv2 Grid Shift File) before it can be used.
Other raster formats like (.tiff) can also be used.
- Download the "Geoid OGD" dataset from Swisstopo under the following link Download Link: Geoid OGD from Swisstopo.
- Unzip the archive to retrieve the file:
chgeo2004_htrans_LV95.agr. -
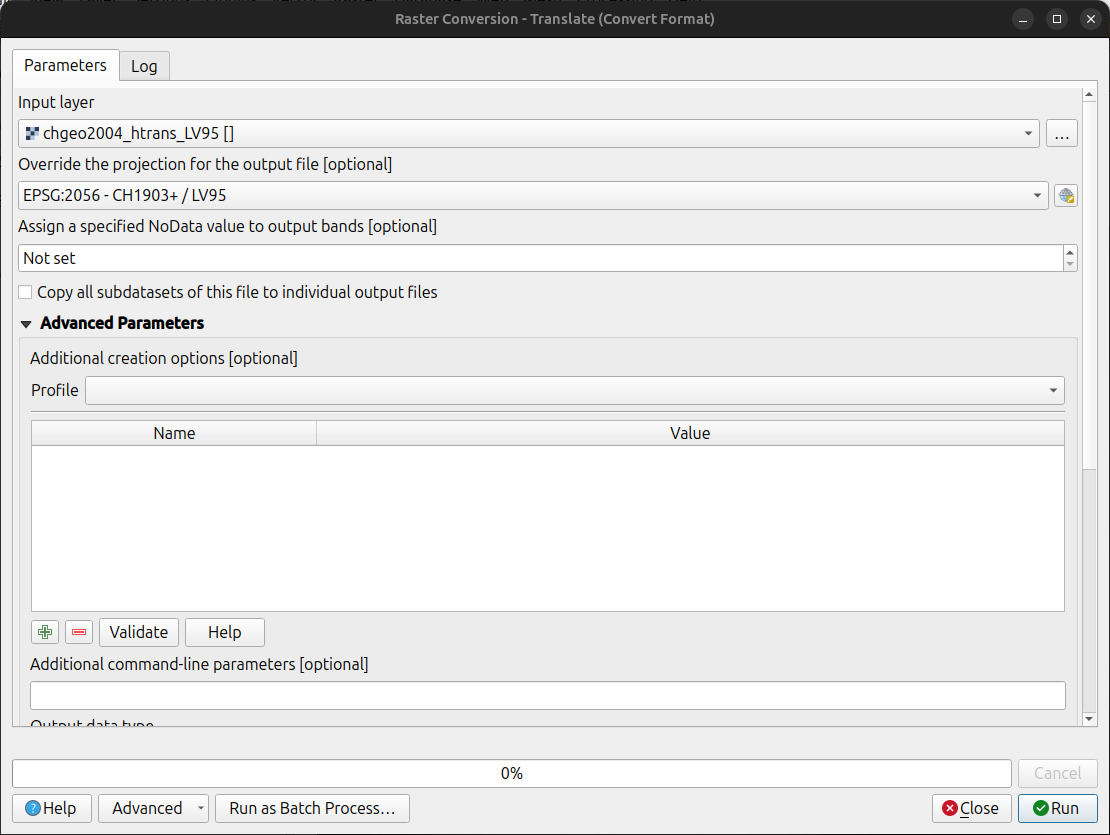
Convert the file using the using the gdal_translate algorithm with one of the following options:
Method 1: QGIS Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- In QGIS, open the Processing Toolbox panel.
- Navigate to GDAL > Raster conversion > Translate (Convert format) tool.
- Configure it with your needed requirements:
- Input layer: Select your
chgeo2004_htrans_LV95.agrfile. - Output file: Click "Save to File..." and name your output file with a
.gtxextension (or other format needed), for example,chgeo2004_htrans_LV95.gtx.
- Input layer: Select your
- Click Run. The other default settings are typically sufficient for this conversion.
Method 2: Command Line (
qgis_process)For automation or users who prefer the command line,
qgis_processis a great option.- Open your terminal and run the following command, adjusting the paths to your files.
qgis_process run gdal:translate --INPUT="/path/to/your/chgeo2004_htrans_LV95.agr" --OUTPUT="/path/to/your/chgeo2004_htrans_LV95.gtx"
Method 3: PyQGIS Script
You can also perform the conversion programmatically within the QGIS Python Console or a standalone script.
import processing input_grid = '/path/to/your/chgeo2004_htrans_LV95.agr' output_grid = '/path/to/your/chgeo2004_htrans_LV95.gtx' processing.run("gdal:translate", { 'INPUT': input_grid, 'OUTPUT': output_grid }) print(f"Successfully converted grid to: {output_grid}")
Fieldwork
-
Copy the
chgeo2004_htrans_LV95.gtxfile to the directory [App Directory]/QField/proj on your mobile device. -
Open the Site Dashboard
-
Tap on the 3-dotted menu (⋮) and direct to Settings > Positioning
-
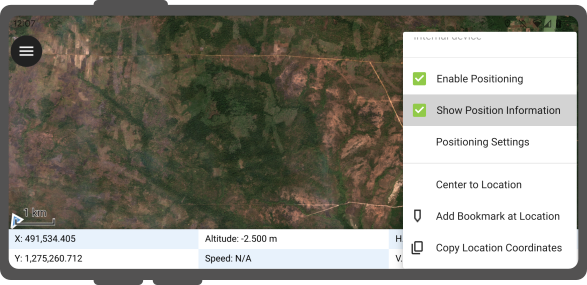
Enable your GNSS device. It will directly center to your current location once the positioning information is available.
-
Change to edit mode and press on the target button - the cross in the center means it is using GNSS positioning.
A long press on the GNSS button will show the positioning menu. Inside the menu you can turn on the Show position information which will show the current coordinates that are reprojected into the CRS of your project along with the precision information.
Note
If you see WGS 84 lat/lon information instead of information in your project CRS, you probably have no signal yet.
Positionierungsvariablen¶
You can get the positioning information both of your internal and external device by specifically configuring your attribute form.
Diese Variablen werden üblicherweise als Teil von Standardwerte-Ausdrücken für Felder verwendet, um die Qualität der einzelnen Messpunkte zu dokumentieren.
A common use case is recording the horizontal accuracy, which can be done by using the variable @position_horizontal_accuracy.
For a complete listing of all available variables, refer to the expression variables reference documentation.
Informationen zum GNSS-Z-Wert bei Verwendung eines Geoids: - Antennenhöhenausgleich=False
| Geoid wird genutzt | Punkt Z Wert z(geometry) | GNSS-Gerät z(@position_coordinate) | QField Anzeige | QField Label |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | Z ellipsoider Wert vom Gerät | Z ellipsoider Wert vom Gerät | Z ellipsoider Wert vom Gerät | Höhe: xxx.xxxx m |
| Orthometrische Höhe des Geräts | Z Orthometrische Höhe des Geräts | Z Orthometrische Höhe des Geräts | Z Orthometrische Höhe des Geräts | Höhe: xxx.xxxx m (ortho.) |
| USER_Shift_Grid.GTX (Geoid) vertical grid shift |
Z Geoid-Wert | Z ellipsoider Wert vom Gerät | Z Geoid-Wert | Höhe: xxx.xxxx m (grid) |
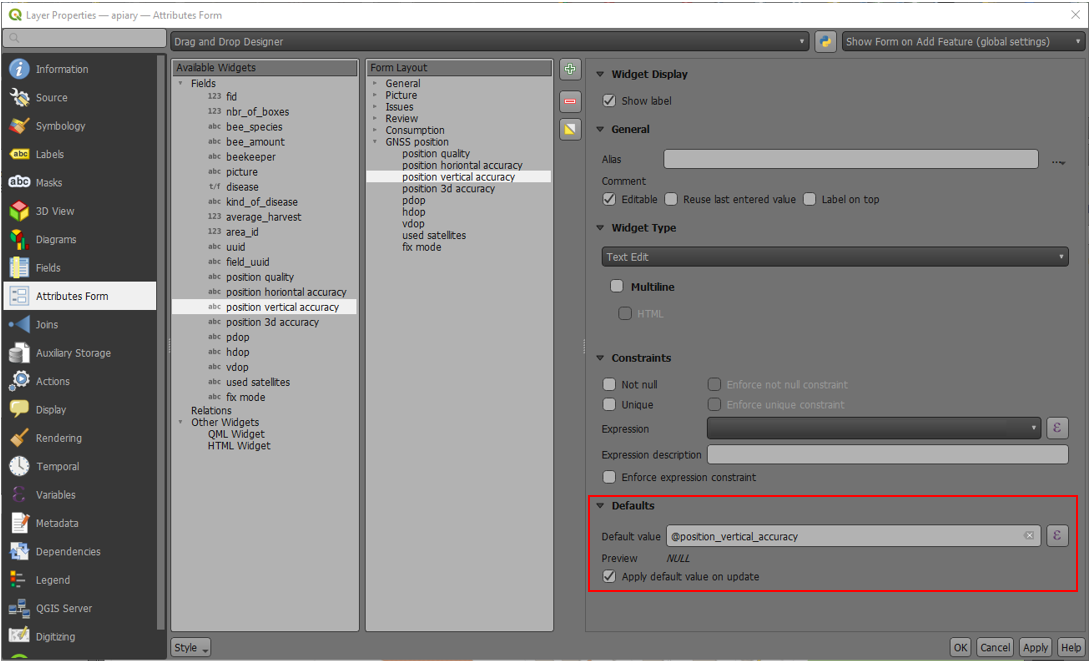
Capturing longitude, latitude and altitude in attribute form¶
It is useful and not uncommon that the actual positioning values should be automatically stored inside the attribute form. This applies for longitude, latitude and altitude.
Workflow
Configuration of attribute form
- In QGIS direct to your Layer Properties > Attribute Form
- (Optional): You have to add a field of decimal type to the form that can capture the data. Name it accordingly (eg. "longitude")
-
Under the settings of the widget display of the corresponding field add the following default value:
- Longitude:
x(@position_coordinate) - Latitude:
y(@position_coordinate) - Altitude:
z(@position_coordinate)
- Longitude:
This will save the coordinate directly in the field when adding a new feature.
Note
This only works if positioning is turned on.
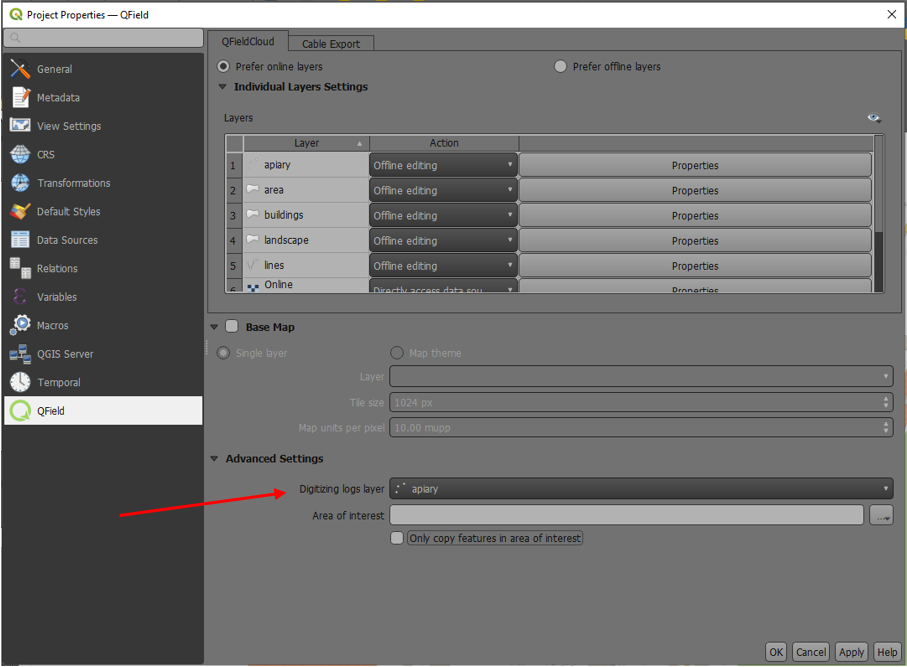
Vertex log layer¶
It is good practice to create a log layer of the collected vertices. It enables you to keep track of the meta data for each vertex like GNSS quality attributes and more.
Workflow
Verwendung eines externen GNSS Empfängers¶
Feldarbeit
QField unterstützt die Verbindung zu externen GNSS-Positionierungsgeräten über NMEA-Streams durch Bluetooth-, TCP, oder UDP-Verbindungen.
Under the Positioning section, you are able to manage and switch between your internal and saved external GNSS devices.
Zusammenfassung der Verbindungsmöglichkeiten nach Betriebssystem:
| Android | iOS | Windows | Linux | MacOS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth | * | ||||
| TCP | |||||
| UDP | |||||
| Serieller Anschluss |
(*) Die Bluetooth-Unterstützung unter Windows erfolgt über die virtuelle serielle Schnittstelle, die das Betriebssystem automatisch erstellt, wenn es eine Verbindung zum GNSS-Gerät herstellt.
Die derzeit unterstützten NMEA-Sätze sind GGA, RMC, GSA, GSV, GST, VTG, HDG und HDT.
Anmerkung
Vergewissern Sie sich, dass keine andere Anwendung wie z. B. ein Mocking Location Provider die gleiche Verbindung verwendet.
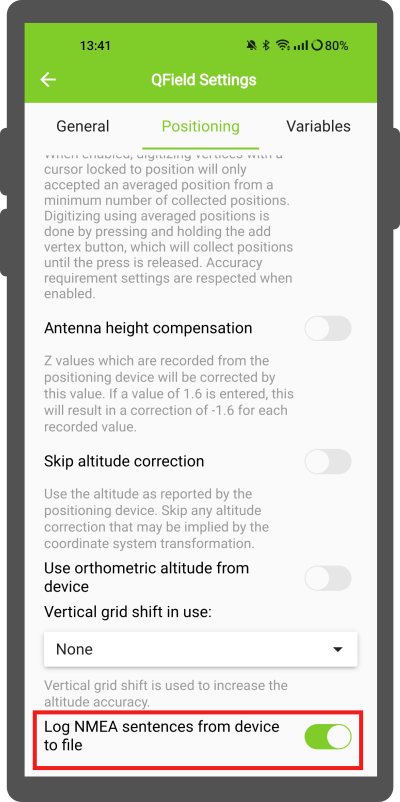
Externes Empfängerprotokoll¶
If you have selected an external receiver as the positioning device, you will find a switch Log NMEA sentences from device to file.
If this is activated, all NMEA sentences coming from external positioning devices will be logged to a file.
The logs will be placed in [App Directory]/QField/logs.
Anmerkung
Beachten Sie, dass das Protokoll, wenn es immer eingeschaltet ist, den Speicherplatz immer weiter füllt.
Mock/Schein-Standort¶
Feldarbeit
Es ist möglich, QField einen Scheinstandort über eine separate Android-App zur Verfügung zu stellen. Hierfür gibt es mehrere Optionen, eine davon ist der [Android NTRIP Client].(https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.lefebure.ntripclient).
Um dies zu nutzen, müssen Sie [Mock Locations auf Ihrem Android-Gerät aktivieren].(https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v1eRHmMiRJQ).
Mittlere Positionierungs-Option¶
Feldarbeit
Note
The coordinate cursor must be locked to the current location via the Lock to position button
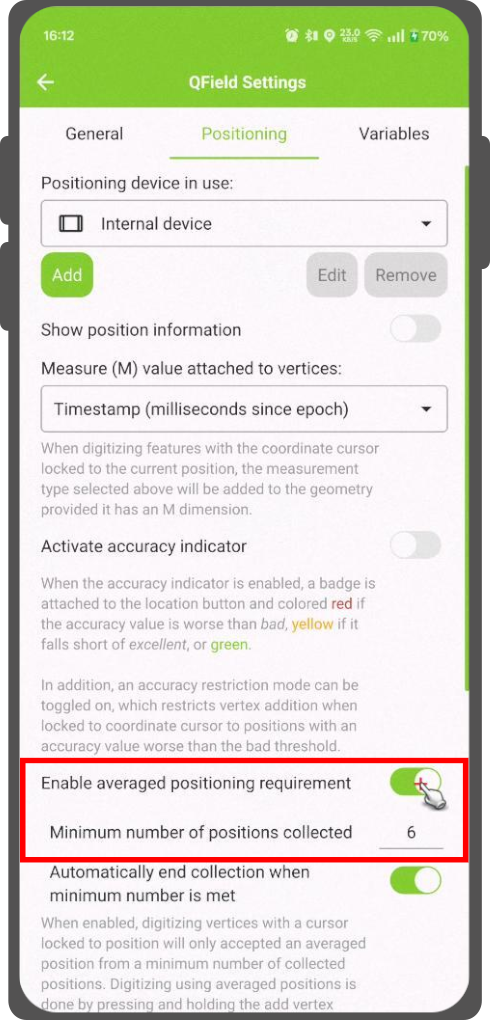
Es gibt eine Funktion, mit der Sie mit gemittelten Positionen digitalisieren können.
Die Aufnahme beginnt mit dem Drücken und Halten der Taste "Scheitelpunkt hinzufügen", wodurch die Erfassung der Positionen beginnt.
During the collection, an indicator will appear on top of the coordinate cursor showing the number number of the collected positions. If an averaged position minimum count requirement is active, a progress bar will also be present indicating the progress towards meeting that requirement.
- To activate direct to side "Dashboard" > Settings > Positioning
- Shortly tap where you want to collect points and QField will automatically add the averaged position once the minimum count is met.
Note
When using @gnss_* or @position_ variables on averaged positions, the variable will also represent the average over all collected samples.