QField 插件¶
QField has a QML/Javascript plugin framework through which additional functionalities and features can be scripted.
插件类型¶
Plugins can be served in two ways:
- 作为项目特定插件,在给定项目会话期间激活;
- 作为应用程序插件,在 QField 启动时激活。
Note
A permission dialog is shown prior to activating a plugin, providing you with the possibility of granting or denying individual plugins.
Project plugins¶
Project plugins are deployed as a sidecar file to a given project file and must share the same file name with a .qml extension. For example, if your project file is “tree_inventory_qfield.qgs”, the plugin’s main QML file must be “tree_inventory_qfield.qml”.
For cloud projects, you simply add the relevant QML file into your local cloud project folder and upload the newly added file on QGIS using qfieldsync. This method insures a smooth plugin deployment and update to devices on the field.
For non-cloud projects, refer to the QField storage handling documentation page to learn how to import projects onto devices.
Application plugins¶
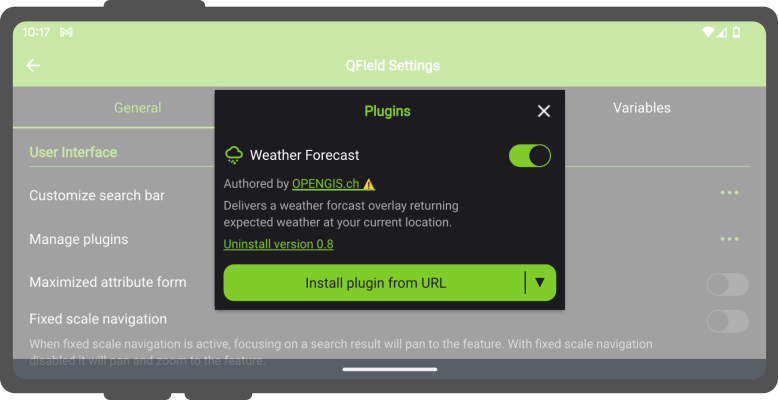
Application plugins are installed through a plugins popup accessed from QField’s Settings panel. Click on the "Install plugin from URL" button and paste in a URL pointing to a zipped plugin file, or download one of the "Available Plugins" already developed by the community.
Once installed, the plugin will appear in the plugins list found in the popup, with a switch to toggle the activation of the plugin.